this post was submitted on 14 Mar 2025
23 points (100.0% liked)
Space
9933 readers
516 users here now
Share & discuss informative content on: Astrophysics, Cosmology, Space Exploration, Planetary Science and Astrobiology.
Rules
- Be respectful and inclusive.
- No harassment, hate speech, or trolling.
- Engage in constructive discussions.
- Share relevant content.
- Follow guidelines and moderators' instructions.
- Use appropriate language and tone.
- Report violations.
- Foster a continuous learning environment.
Picture of the Day
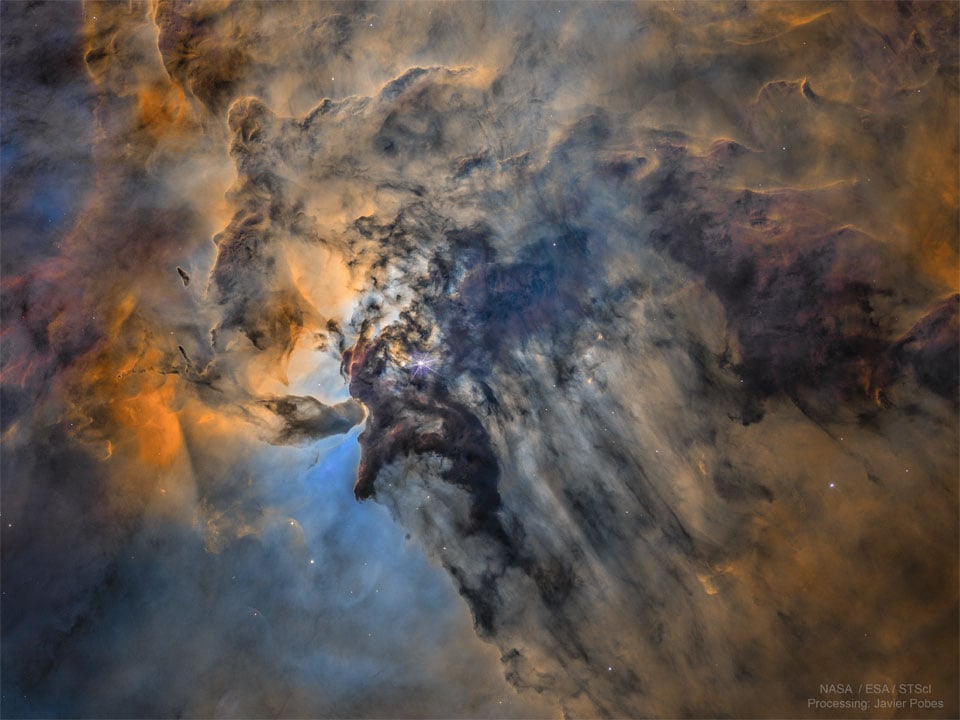 The Busy Center of the Lagoon Nebula
The Busy Center of the Lagoon Nebula
Related Communities
🔭 Science
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
🚀 Engineering
🌌 Art and Photography
Other Cool Links
founded 2 years ago
MODERATORS
you are viewing a single comment's thread
view the rest of the comments
view the rest of the comments

For the same reason the moon is red and not black: The earth's atmosphere is scattering and bending sunlight. Red light scatters the least, and ends up with the smoothest distribution once it's past by the planet, while bluer light scatters more frequently, and will be more effectively blocked.
Not that "more effectively" is not the same as "totally". This leaves the outer regions of the umbra receiving more light -- and less reddened light -- than the centre of the umbra.
So like the umbra has a "bright" edge compared to its center?
I think that was my mistake, I was thinking of the transition between the penumbra and umbra had a straigt edge when viewed from earth.
thanks
Yes, but it's not just brighter near the outer edges, it's whiter, thanks to the inclusion of more blue light, and that less ruddy colour does a lot to affect how we see the gradation from light to dark.
They are harder to find than they should be, but there are pictures of the Earth occulting hte sun out there, and you can see how the Earth's atmosphere is aglow with scattered sunlight. There's more light closer to where the sun is than where isn't. The Blue Ghost lander pictures of the eclipse are probably the most accessible right now:
The bright ring around the Earth in ths image is sunlight streaming through the Earth's atmosphere. See how blue it looks? And how it gets brighter closer to the sun?
That's why.
Got it, thats very interesting. I already understood the redness of the shadow but had no idea how much more complex it is and that picture of earth eclipsing the sun makes it way more clearer.
Thank you very much, I would upvote you 10 times if I could.