this post was submitted on 02 Feb 2025
86 points (69.2% liked)
Space
9190 readers
16 users here now
Share & discuss informative content on: Astrophysics, Cosmology, Space Exploration, Planetary Science and Astrobiology.
Rules
- Be respectful and inclusive.
- No harassment, hate speech, or trolling.
- Engage in constructive discussions.
- Share relevant content.
- Follow guidelines and moderators' instructions.
- Use appropriate language and tone.
- Report violations.
- Foster a continuous learning environment.
Picture of the Day
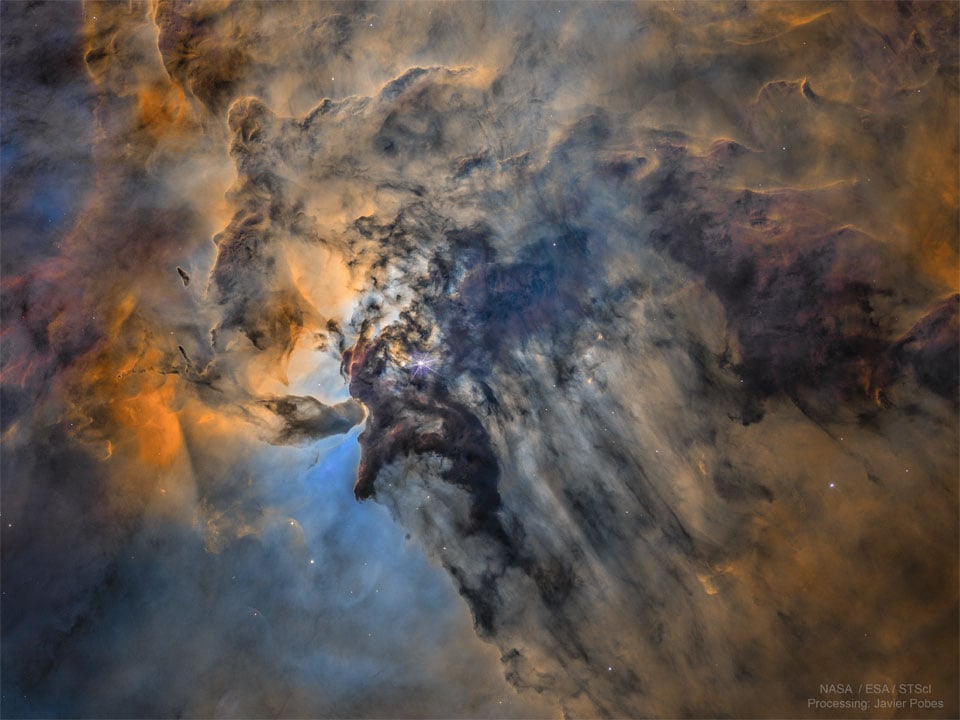 The Busy Center of the Lagoon Nebula
The Busy Center of the Lagoon Nebula
Related Communities
🔭 Science
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
🚀 Engineering
🌌 Art and Photography
Other Cool Links
founded 2 years ago
MODERATORS
you are viewing a single comment's thread
view the rest of the comments
view the rest of the comments

not possible. This could work for orbiting probes but only if you send up a little fuel with it as well. The orbital mechanics work out so that the probe will fall to the height of the catapult which is in the atmosphere.
What prevents them from doing exactly that?
Lots of (all?) satellites have propulsion systems to make orbit adjustments anyway. Is it that complicated to bolster them a bit for that purpose?
I'd imagine having the propellant tanks, plumbing, valves and engines survive 10,000Gs without crumpling or deforming to the point of failure is going to be a bit of an issue. Any thin and lightweight structures like foldable solar panels (and their deployment mechanisms) are also going to be tricky.
Hmm, but if the acceleration is gradual, shouldn't it be fine?
Or are you referring to the constant centripetal acceleration felt by the object as it's spinning?
Man is physics class far away
The centripetal acceleration. It's going to ramp up fast. There's also the concern of what's gonna happen to the payload when it's released, exits the vacuum chamber and smacks right the fuck into the dense low-level atmosphere at a significant Mach number. Cause that's what has to happen if the goal is to reduce the need for onboard propellant.
Well I just meant the restriction in the title where it said no rocket fuel. Its not possible if you have no rocket fuel. But they probably will use rocket fuel if they get the faucility to have a big enough diameter to get mostly to orbit.